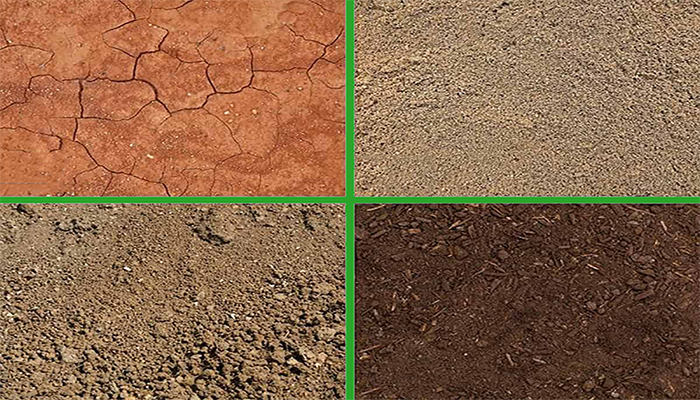
Understanding the different types of soil is essential for anyone involved in gardening, farming, or landscaping. Soil plays a crucial role in the growth and development of plants, and different plants thrive in different soil conditions. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the secrets of soil types, exploring their characteristics, uses, and the best plants to grow in each type. Whether you are a seasoned gardener or just starting out, this guide will provide you with the knowledge you need to make informed decisions about your soil.
Table of Contents
Importance of Understanding Different Soil Types
The importance of understanding different soil types cannot be overstated. Each soil type has unique properties that directly impact plant growth. By understanding the characteristics of different soils, you can choose the right plants for your garden, improve soil fertility, and enhance the overall health of your plants. Additionally, knowledge of soil types can help you identify and address common soil-related issues such as poor drainage, nutrient deficiencies, and soil erosion.
Classification of Soil Types
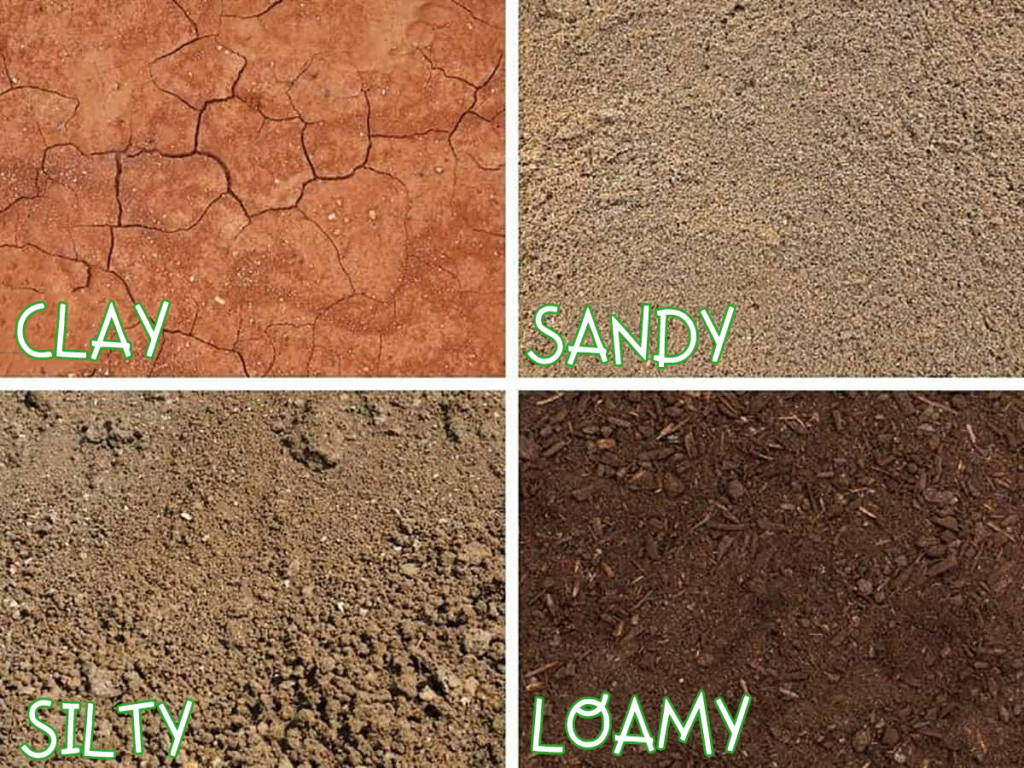

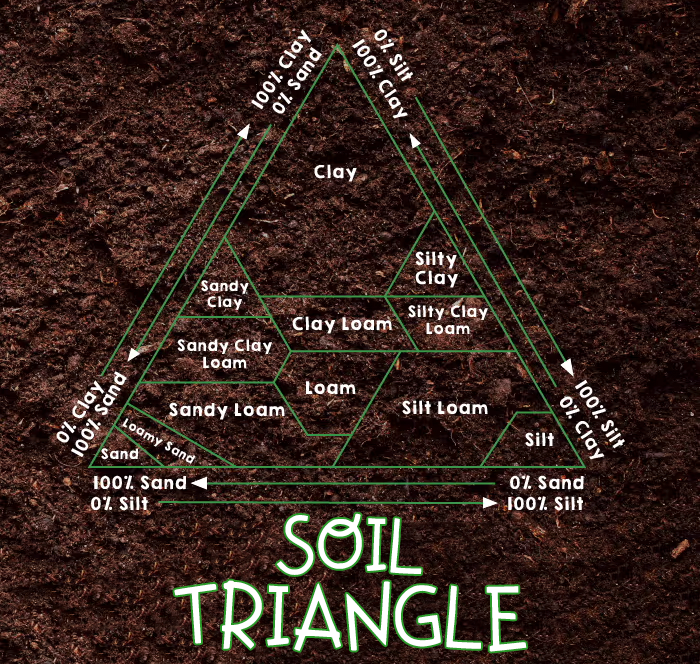
Soil types can be classified into several categories based on their composition and texture. The most common soil types include sandy soil, clay soil, loamy soil, peaty soil, chalky soil, and silt soil. Each of these soil types has distinct characteristics that influence its ability to retain water, drain effectively, and provide essential nutrients to plants.
Sandy Soil – Characteristics and Uses
Sandy soil is characterized by its gritty texture and poor water retention. It is composed of large particles that allow water to drain quickly, making it ideal for plants that prefer dry conditions. However, sandy soil often lacks essential nutrients and requires regular fertilization. Despite its drawbacks, sandy soil is excellent for growing root vegetables such as carrots and radishes, as well as drought-tolerant plants like cacti and succulents.
Clay Soil – Characteristics and Uses
Clay soil is composed of tiny particles that compact together, resulting in poor drainage and a tendency to become waterlogged. However, clay soil has excellent nutrient-holding capacity, making it fertile and suitable for a wide range of plants. To improve drainage in clay soil, organic matter such as compost or peat moss can be added. Plants that thrive in clay soil include sunflowers, irises, and certain types of fruit trees.
Loamy Soil – Characteristics and Uses
Loamy soil is considered the ideal soil type for gardening, as it combines the best qualities of sandy and clay soils. It has a balanced texture that allows for proper drainage while retaining essential moisture and nutrients. Loamy soil is rich in organic matter and provides an excellent environment for plant roots to grow and spread. This type of soil is suitable for a wide variety of plants, including vegetables, flowers, and shrubs.
Peaty Soil – Characteristics and Uses
Peaty soil is characterized by its high organic matter content, which gives it a dark, spongy texture. It is typically found in wetland areas and retains moisture well. Peaty soil is acidic and nutrient-rich, making it suitable for acid-loving plants such as rhododendrons, blueberries, and ferns. However, due to its high water-holding capacity, it may require additional drainage for some plants.
Chalky Soil – Characteristics and Uses
Chalky soil, also known as alkaline soil, is characterized by its high pH level and presence of calcium carbonate. It is often pale and stony and tends to drain quickly. Chalky soil is not suitable for plants that prefer acidic conditions, but it is ideal for growing alkaline-loving plants such as lavender, rosemary, and clematis. To improve the fertility of chalky soil, organic matter and fertilizers can be added.
Silt Soil – Characteristics and Uses
Silt soil has a fine, smooth texture and is composed of small particles. It has good water retention properties while still providing adequate drainage. Silt soil is fertile and easy to work with, making it suitable for a wide range of plants. However, it can compact easily, leading to poor aeration. Regular cultivation and addition of organic matter can help improve the structure of silt soil. Plants that thrive in silt soil include lettuce, spinach, and beans.
Understanding pH Levels in Different Soil Types
pH levels play a crucial role in plant growth, as they determine the availability of essential nutrients in the soil. Different plants have different pH preferences, and understanding the pH levels of your soil is essential for selecting the right plants. Most plants prefer a slightly acidic to neutral pH range, typically between 6 and 7. However, some plants, such as blueberries and azaleas, thrive in more acidic conditions, while others, like lilacs and asparagus, prefer slightly alkaline soil. Conducting a soil test can help determine the pH level of your soil and guide you in selecting plants accordingly.
Improving Soil Fertility and Structure
Regardless of the soil type, there are several ways to improve its fertility and structure. Adding organic matter, such as compost or well-rotted manure, can enrich the soil with essential nutrients and improve its ability to retain moisture. Mulching is another effective technique that helps conserve moisture, suppress weeds, and gradually improve the soil as the organic matter decomposes. Regularly rotating crops and practicing crop rotation can also help prevent nutrient depletion and reduce the risk of disease and pest infestation.
Best Plants for Different Soil Types
Choosing the right plants for your soil type is crucial for successful gardening. While some plants can adapt to different soil conditions, many have specific preferences. Sandy soil is well-suited for plants like lavender, rosemary, and succulents.
Clay soil is ideal for sunflowers, irises, and tomatoes.
Loamy soil is perfect for a wide range of plants, including tomatoes, roses, and beans.
Peaty soil is best for rhododendrons, blueberries, and ferns. Chalky soil is suitable for lavender, rosemary, and clematis.
Silt soil is excellent for lettuce, spinach, and potatoes.
By selecting plants that are adapted to your soil type, you can ensure healthy growth and bountiful harvests.
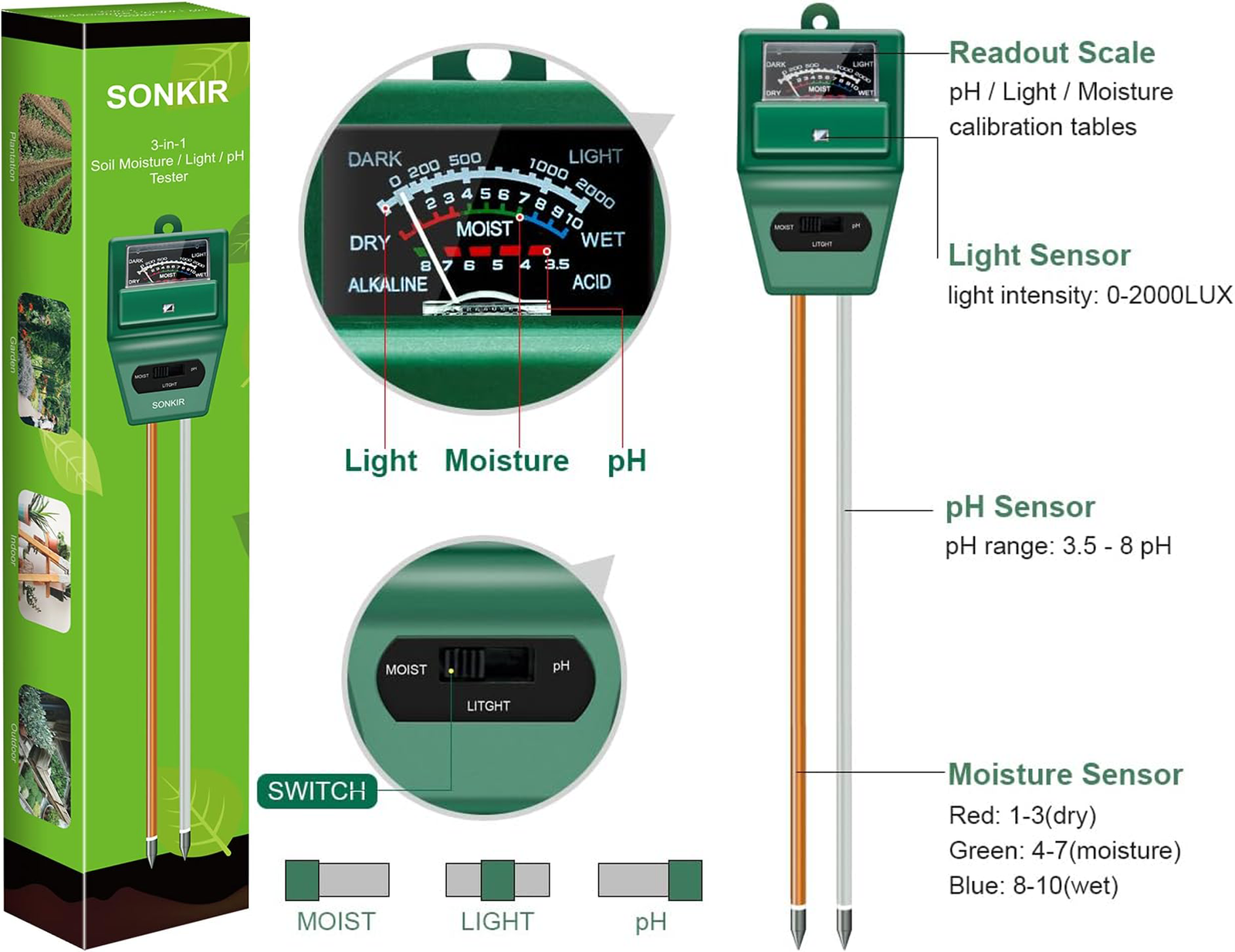
Testing Your Soil:
Before planting, it’s beneficial to test your soil to understand its pH level and nutrient content. Soil test kits are available on amazon

Conclusion
Understanding the different types of soil is essential for any gardener or farmer. By familiarizing yourself with the characteristics and uses of various soil types, you can make informed decisions about your gardening practices and enhance the health and productivity of your plants. Whether you have sandy soil, clay soil, loamy soil, peaty soil, chalky soil, or silt soil, there are plants that will thrive in your garden. By improving soil fertility and structure, and selecting the right plants for your soil type, you can create a flourishing garden that brings you joy and satisfaction for years to come.
CTA: Start exploring your soil type and plant the right seeds for a fruitful garden. Remember, knowledge is the key to successful gardening!
You might also be interested in:


